Financial Engineer/ Financial Mathematician
Entry Level Qualification
12
Career Fields
Banking & Finance
For Specially Abled







About Career
PARTICULARS | DESCRIPTION |
Name | Financial Engineer/ Financial Mathematician |
Purpose | develop financial products |
Career Field | Banking & Finance |
Required Entrance Exam | CAT, XAT, MAT |
Average Salary | 600000 - 2500000 Rs. Per Year |
Companies For You | Goldman Sachs, Barclays, and AIG & Many More |
Who is Eligible | Graduate |
1. As a Financial Engineer/ Financial Mathematician, you will be part of a cross-functional team which is involved in conducting statistical & mathematical deductions using various formula and methods. You will also write or build and use various mathematical/ financial modeling techniques to accurately describe financial situations, economic relations, financial market dynamics, investment flows, financial risks, taxation efficacies, and other relevant issues of practical significance in the financial and economic realm.
2. You will be using various statistical, data analytical, and financial software to carry out your work. You will write or build different mathematical and financial models as well as algorithm (a set of rules used in calculations or computing or other problem-solving operations using a computer) to solve complex financial problems using computers.
3. You will write or build different mathematical and financial models as well as algorithms to predict various future scenarios in the financial and economic realm or space. For example, predicting how the price of a stock (equity share of a company) may change over time; how currency exchange rate may change over time (exchange rate means at the rate in which currency is converted, for example from Indian Rupee to US Dollar); how economic growth rate may change over the next 3 years; out of the total number of people who have a particular health insurance policy, how many people may make a claim over the next 10 years; and so on.
Brief about possible duties
You will have to apply your expertise in forecasting, quantitative analysis, data science, scenario modeling and data visualization. You will also have to collate, assess, analyze, present, report and communicate data/ results, along with implications. These data/ results will be generated through stochastic analyses (analyzed statistically but not predicted precisely), mathematical modeling, and financial modeling. You will have to report these through many means such as online reporting, analytical reports, financial presentations, presentations at conferences, etc. for a variety of audiences using visual tools that can effectively communicate the story behind the numbers.
What is forecasting?
Now, “forecasting” (which will be a regular responsibility), in this case, means to predict future trends of events that may happen specifically due to certain finance-related decisions, allocation of resources or economic relationships, etc.
What is financial modeling?
Financial modeling means writing or developing a set of rules/formulas and algorithms for solving a financial problem or carry out some calculations using financial theories, concepts, and formulas. Such rules/formulas and algorithms are executed using computer software.
What is mathematical modeling?
Mathematical modeling implies using linear algebra, natural logarithms, calculus, statistics, and the concepts of relations & functions to achieve a particular result or to determine the factors playing a part in an event (such as the rise/ fall of wages or stock price and valuation etc.) or to estimate the values of such factors/ parameters.
The numbers are always drawn from existing real-time values to create huge datasets and apply statistical hypothesis testing to forecast future possibilities.
What is statistical hypothesis testing?
Statistical hypothesis testing or confirmatory data analysis uses a set of random variables, the variations of which are used to test whether a particular “hypothesis” or the basis of observing a process is true or untrue.Commonly, two datasets are compared where usually one is formed through collecting data (called “sampling”) and the other is a synthetic data set from an idealized model.
Some popular techniques
Understand that, you will be involved in using financial and mathematical modeling for forecasting via assessing of large repetitive real-life datasets containing numbers gathered from real-time scenarios to prove a particular point using tools used widely in Mathematics and Statistics such as Random Walks, Monte-Carlo simulation, fuzzy logic, decision tree models, neural network models, linear regression models, Fourier transform, representation theory etc.
Intricate and extensive concepts
These intricate & extensive techniques require profound understanding and knowledge before being logically applied to real existing cases. This further means that professionals practicing in this field are highly qualified individuals with expansive experience in particular academic areas especially Economics, Mathematics or Statistics.
Today, most investment decisions are driven by a pre-programmed set of instructions (algorithms) fixed in a suite of financial software.
1. These algorithms, that fuel what is universally called algorithmic trading today, come from financial models with different dependent & independent variables such as time, price, and volume. These are commonly called parameters. What investment managers do is just set the values of the variables or parameters in the software.
2. The software then takes automated decisions to carry out transactions (buy and sell stocks, bonds, currencies, etc.). This automated trading is therefore called algorithmic trading.
3. This is currently the hottest area in which Financial Engineers/ Mathematicians are finding work with just engineering degrees / Mathematics / Statistics degrees. No prior background in Finance is required.
Algorithmic Trading –how financial modeling is used in making investment decisions in stock markets
1. Algorithmic trading, automated trade execution and high-frequency trading (HFT-execute a very large number of orders within seconds) at the millisecond timescale were developed to make use of the speed & data processing advantages that computers have over humans. In the 21st century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders.
2. It is widely used by investment banks, pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds that may need to perform trades too fast for human traders to react to. In India, 33.33% of the exchange trades are done through algorithmic trading. In the US, it is 70% and in Europe 40%.
In simpler terms
Stock trading was mainly a paper-based activity before electronic trading took over. One needed to be physically present to buy or sell stocks and there were actual stock certificates.
Now, we can write an algorithm and instruct a computer to buy or sell stocks for you when the defined conditions are met. These programmed computers can trade at a speed and frequency that is impossible for a human trader. So now there are markets in which computers trade against other computers.
4 Components of Algorithmic Trading Systems
Data Component
Algorithmic Trading systems use structured data, unstructured data, or both. Structured data includes spreadsheets, CSV files, XML, Databases, etc. Inter-day prices, end of day prices, and trade volumes are usually available in a structured format. Unstructured data include news, social media, videos, and audio.
Model Component
Financial models represent how the algorithmic trading system believes the markets (or the outside world) work. These financial models do one common thing: reducing a complex system into a quantifiable set of rules which describe the behavior of that system under different scenarios.
Execution Component
The model component identifies certain trades and the execution component carries out or performs the transactions. The speed of the execution, the frequency at which trades are made, the period for which trades are held, etc. are factors that need to be satisfied.
Monitor Component
The monitor component is powered by AI basically to make the entire algo trading system adapt to the dynamism of the markets and changing environments.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
As a financial Engineer/ Financial Mathematician, you will be engaged with one or more of the following roles & responsibilities as well as other associated duties:
1. You will apply mathematical or statistical techniques to address issues of practical significance in finance, such as assets valuation, securities trading, investment management, or market regulation.
2. You will investigate methods for financial analysis to create mathematical models used to develop improved analytical tools or advanced financial investment instruments.
3.You will research or develop analytical tools to address issues such as equity portfolio optimization, performance measurement, profit & loss measurement, or pricing models.
4.You will apply your expertise in forecasting, quantitative analysis, data science, scenario modeling and data visualization to help optimize workforce strategy (acquire, retain, develop, motivate & deploy human capital) or assist in increasing/ sustaining shareholders’ interests.
5. You will develop core financial models, using advanced statistical, quantitative, or econometric techniques.
6. You will devise or apply independent tools and techniques for verifying results of analytical procedures.
7. You will collaborate with data engineering & visualization engineers to access and manipulate data, explain data gathering requirements, and display results
8. You will collaborate with product development teams to research, model, validate, or implement quantitative structured solutions for various types of markets economies.
9. You will confer with market experts or analysts on trading strategies, market dynamics or performance for the development of quantitative techniques.
10.You will collate, assess, analyze, present, report and communicate data/ results, along with implications, generated through stochastic analyses (analyzed statistically but not predicted precisely), financial modeling and mathematical modeling through online systems, creating reports, corporate financial presentations, presentations at conferences, etc. for a variety of audiences using visual, recommendation-oriented tools that communicate the story behind the numbers.
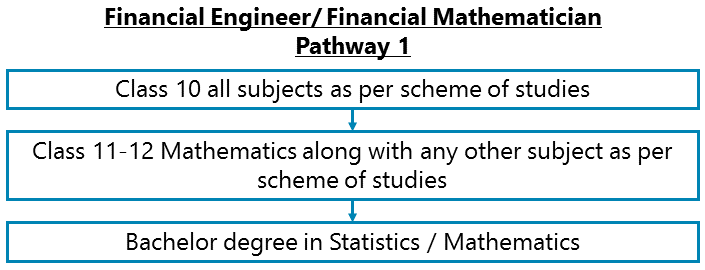
Career Entry Pathway
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies – Bachelor degree in Statistics / Mathematics
After completing Class 11-12 Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for Bachelor degree in Statistics / Mathematics. Prior knowledge of Finance is not required always. The opportunities are few though unless you are passing out from a premier institution like ISI.
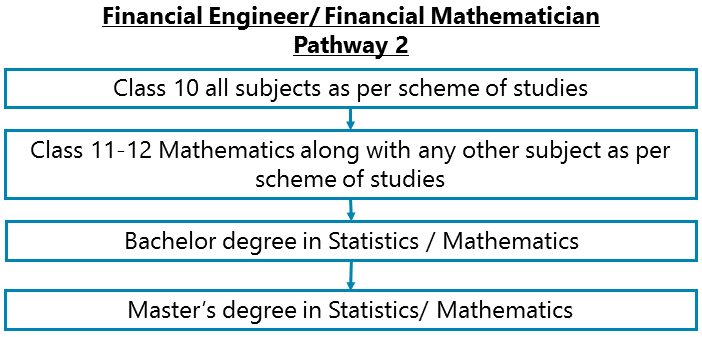
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies – Bachelor degree in Statistics / Mathematics – Master’s degree in Statistics/ Mathematics
After completing Class 11-12 with Mathematics & any other subject as per scheme of studies and a Bachelor degree in Statistics / Mathematics, you can go for a Master’s degree in Statistics/ Mathematics.
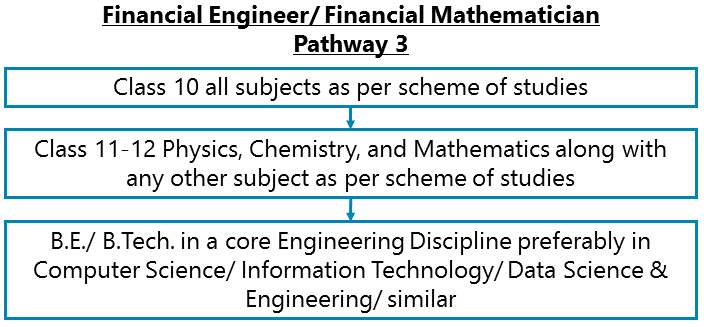
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies – B.E./ B.Tech. in a core Engineering Discipline preferably in Computer Science/ Information Technology/ Data Science & Engineering/ similar
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for B.E./ B.Tech. in a core Engineering Discipline preferably in Computer Science/ Information Technology/ Data Science & Engineering/ similar. The opportunities are few though unless you are passing out from a renowned Engineering institute/University such as the IITs, NITs, BITS Pilani, etc.
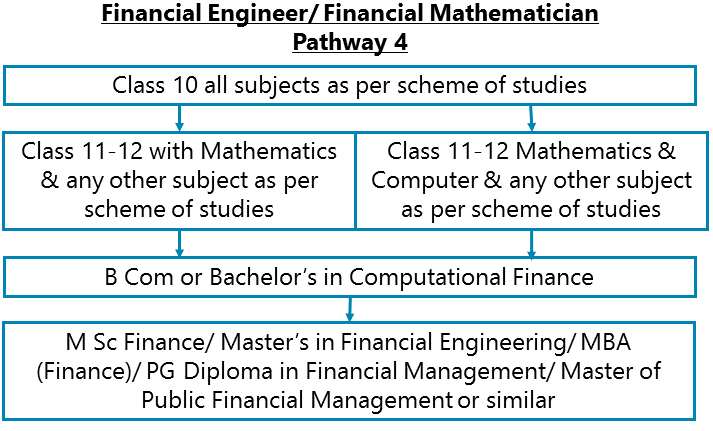
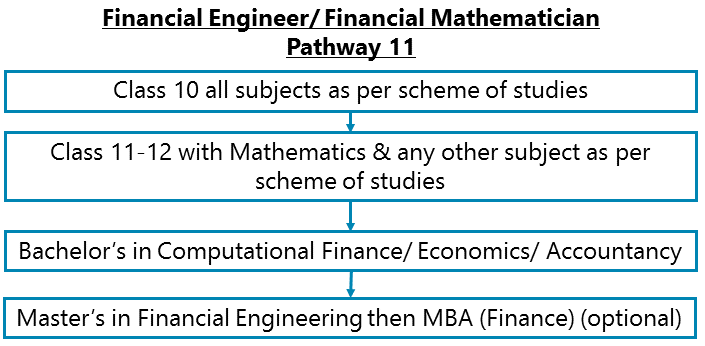
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 with Mathematics and/or Computer & any other subject as per scheme of studies - B Com or Bachelor’s in Computational Finance – M Sc Finance/ Master’s in Financial Engineering/ MBA (Finance)/ PG Diploma in Financial Management/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar
After completing Class 11-12 with Mathematics and/or Computer & any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for B Com or Bachelor’s in Computational Finance. Thereafter pursue M Sc Finance/ Master’s in Financial Engineering/ MBA (Finance)/ PG Diploma in Financial Management/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar.
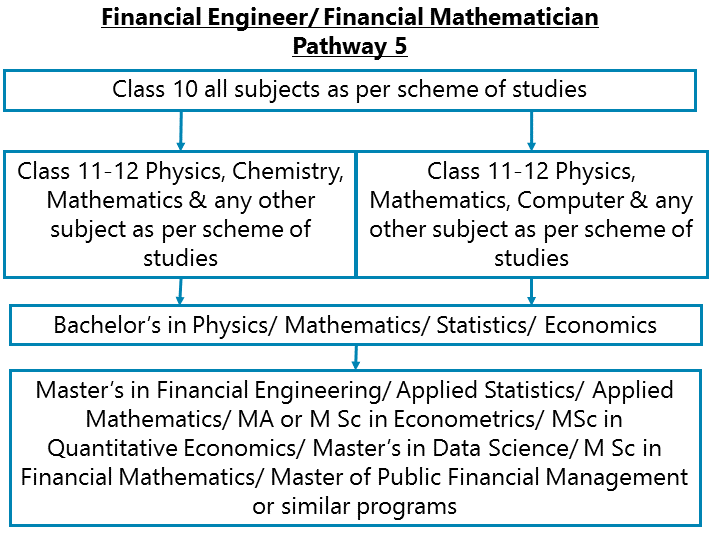
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, Computer and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - Bachelor’s in Physics/ Mathematics/ Statistics/ Economics – Master’s in Financial Engineering/ Applied Statistics/ Applied Mathematics/ MA or M Sc in Econometrics/ MSc in Quantitative Economics/ Master’s in Data Science/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar programs
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry (optional), Computer (optional) and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for Bachelor’s in Physics/ Mathematics/ Statistics/ Economics. Thereafter go for Master’s in Financial Engineering/ Applied Statistics/ Applied Mathematics/ MA or M Sc in Econometrics/ MSc in Quantitative Economics/ Master’s in Data Science/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar programs. Then you may also go for an MBA with specialization in Finance or Marketing Communications or similar.
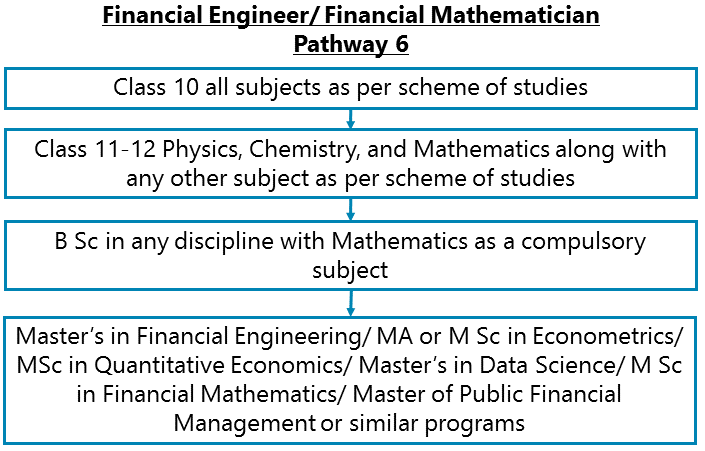
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - B Sc in any discipline with Mathematics as a compulsory subject - Master’s in Financial Engineering/ MA or M Sc in Econometrics/ MSc in Quantitative Economics/ Master’s in Data Science/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar programs
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, go for B Sc in any discipline with Mathematics as a compulsory subject. Thereafter go for Master’s in Financial Engineering/ MA or M Sc in Econometrics/ MSc in Quantitative Economics/ Master’s in Data Science/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master of Public Financial Management or similar programs. Then you may also go for an MBA with specialization in Finance or Marketing Communications or similar.
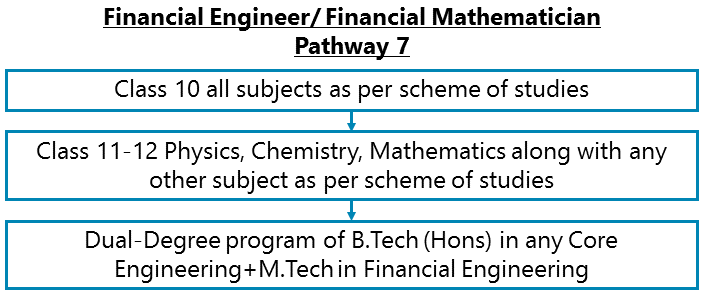
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - Dual-Degree program of B.Tech (Hons) in any Core Engineering+M.Tech in Financial Engineering
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for a Dual-Degree program of B.Tech (Hons) in any Core Engineering+M.Tech in Financial Engineering.
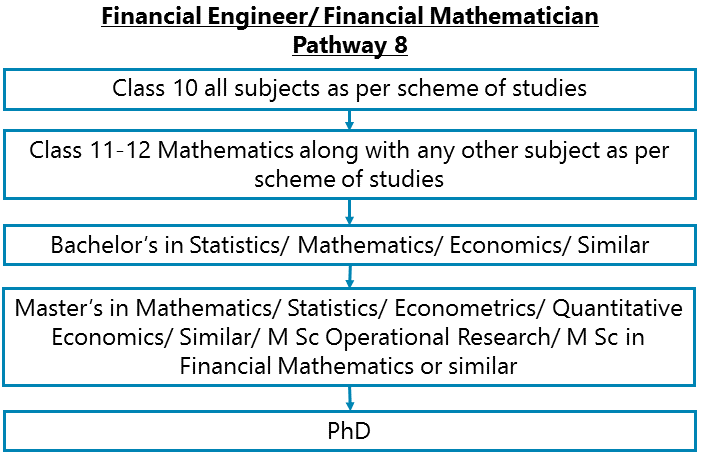
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 with Mathematics & any other subject as per scheme of studies – Bachelor’s in Statistics/ Mathematics/ Economics/ Similar– Master’s in Mathematics/ Statistics/ Econometrics/ Quantitative Economics/ Similar/ M Sc Operational Research/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics or similar - PhD
After completing Class 11-12 with Mathematics & any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for a Bachelor’s in Statistics/ Mathematics/ Economics/ Similar. Then go for Master’s in Mathematics/ Statistics/ Econometrics/ Quantitative Economics/ Similar / M Sc Operational Research/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics or similar. Then you may also choose to complete your Doctoral studies (PhD) in a relevant discipline among banking & decisions making, applied econometrics, risk & derivatives management, capital market, modeling & pricing of commodity derivatives, mergers & acquisitions, earnings management, value relevance of financial numbers or other areas.
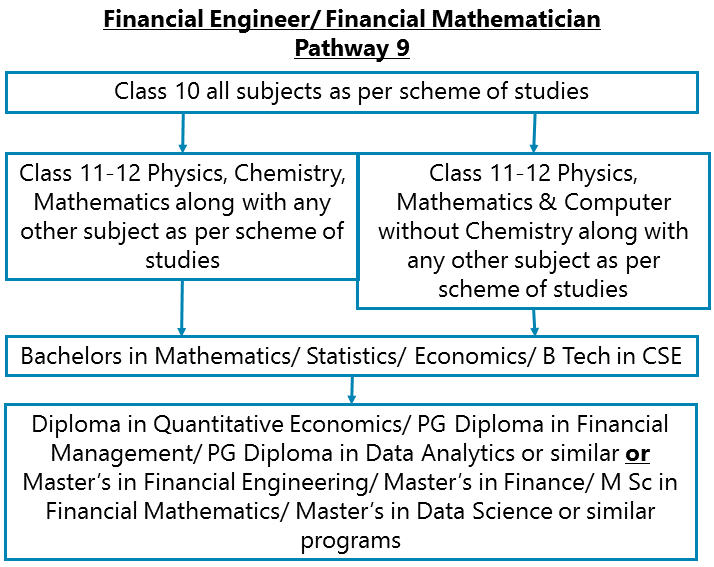
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies - Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, Computer (optional) and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - Bachelors in Mathematics/ Statistics/ Economics/ B Tech in CSE– Diploma in Quantitative Economics/ PG Diploma in Financial Management/ PG Diploma in Data Analytics or similar or Master’s in Financial Engineering/ Master’s in Finance/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master’s in Data Science or similar programs
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, Computer (optional) and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for Bachelor’s in Mathematics/ Statistics/ Economics/ B Tech in Computer Science Engineering. Some colleges offer B Tech in CSE with specialization in BFSI too. Thereafter go for a Diploma in Quantitative Economics/ PG Diploma in Financial Management/ PG Diploma in Data Analytics or similar. Instead of a Diploma, you may go for a Master’s in Financial Engineering/ Master’s in Finance/ M Sc in Financial Mathematics/ Master’s in Data Science or similar programs. Instead of Diploma or Master’s degree as mentioned, may also go for an MBA with specialization in Finance or Marketing Communications.
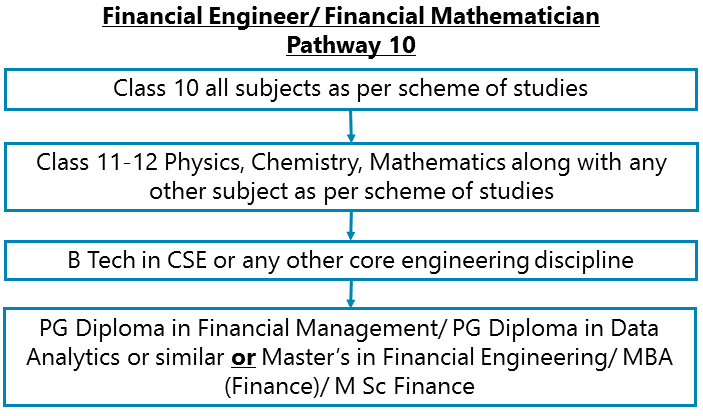
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - B Tech in CSE or any other core engineering discipline – PG Diploma in Financial Management/ PG Diploma in Data Analytics or similar or Master’s in Financial Engineering/ MBA (Finance)/ M Sc Finance
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for B Tech in Computer Science Engineering or any other core engineering discipline. Then go for a PG Diploma in Financial Management/ PG Diploma in Data Analytics/ PGDBA (PG Dip in Business Analytics) or similar. Instead of a PG Diploma, you may also go for a Master’s in Financial Engineering/ M Sc Finance/MBA (Finance)or similar.
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies - Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, Computer (optional) and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - B Tech - PG diploma/ Master's
After completing Class 11-12 Physics, Chemistry, Computer (optional) and Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for B Tech in Computer Science Engineering or any other core engineering discipline. Then go for a PG Diploma in Financial Management/ PG Diploma in Data Analytics/ PGDBA (PG Dip in Business Analytics) or similar. Instead of a PG Diploma, you may also go for a Master’s in Financial Engineering/ M Sc Finance/MBA (Finance)or similar.
Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies – Class 11-12 Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies - B Com – M Com – PhD
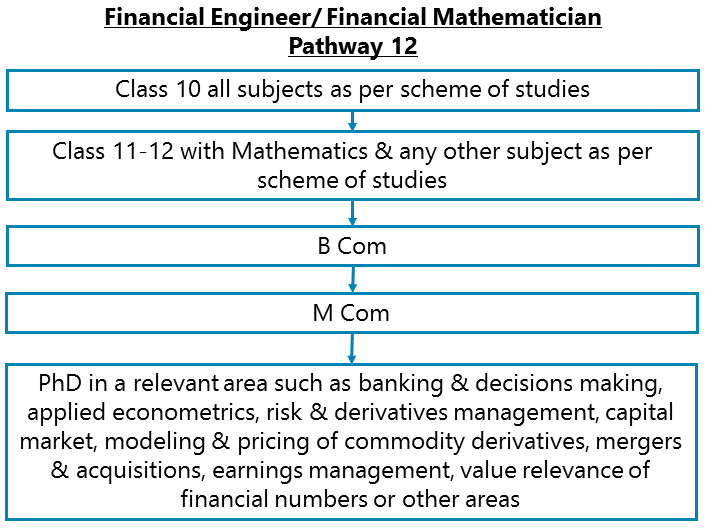
After completing Class 11-12 Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies, you can go for a Bachelor’s in Commerce and then a Master’s in Commerce followed by your Doctoral studies (PhD) in a relevant area such as banking & decisions making, applied econometrics, risk & derivatives management, capital market, modeling & pricing of commodity derivatives, mergers & acquisitions, earnings management, value relevance of financial numbers or other areas.
Required Qualification & Competencies
To get into this field, you will need to pass Class 10 all subjects as per scheme of studies. Then you must complete Class 11-12 with:
1. Physics. Chemistry, Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies
2. Physics. Chemistry, Mathematics, Computer Science along with any other subject as per scheme of studies
3. Mathematics along with any other subject as per scheme of studies
After Class 11-12:
1. You can go for a Bachelor’s in any of the core engineering fields.
2. Bachelor degree in Mathematics, Statistics, Economics, Physics, Accountancy
3. You can go for a Bachelor’s degree in Commerce
4. You can go for a Bachelor’s in Computational Finance
5. You can go for B Tech in Computer Science Engineering with specialization in BFSI
6. You can go for a Dual-Degree program of B.Tech (Hons) in any Core Engineering+M.Tech in Financial Engineering.
7. You can go for a B Sc in any discipline with Mathematics as a compulsory subject.
8. You can obtain Associate Membership/ Fellowship of Institute of Actuaries of India:
9. You will need to pass ACET (Actuarial Common Entrance Test) exam conducted by IAI and some subsequent exams to practice as a qualified Actuary in India. IAI is the globally recognized Institute of Actuaries of India.
10. The minimum required qualification for ACET exam is a pass in Class 11-12. You can also apply for it before your board exam results are announced. You can appear for IAI ACET examination even from outside India.
11. Typically, students pass a couple of IAI exams after ACET and start looking for a job. You can continue with the other papers while on the job. Currently, there are 1426 student members who still have 14 exams to write (to attain fellowship status) but are already on their respective jobs and as in March 2019, there are only 439 Fellows who have passed from IAI after completing all sets of all exams.
12. You can also opt for B Sc and M Sc in Actuarial Sciences / Actuarial Sciences & Analytics but you will have to obtain membership of IAI under all circumstances through ACET followed by some subsequent exams and then practice as an Actuary.
You can appear for other examinations conducted by organizations of other countries such as South Africa (Actuarial Society of South Africa), US and UK (Institute and Faculty of Actuaries-IFoA). US has two governing bodies in this field viz. Casualty Actuarial Society CAS (non-life: property and casualty insurance) and Society of Actuaries (life, health, pensions and retirement). If you have passed in at least 3 subjects under the examination systems of these 3 countries, you are exempt from ACET and can continue with the subsequent exams.
1. You can additionally opt for globally recognized professional certificates and credentials such as
2. The Certificate in Quantitative Finance (CQF)
3. Financial Risk Manager (FRM)
4. Chartered Alternative Investment Analyst (CAIA)
5. Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)
6. Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
7. Associate or Fellow of the Institute of Actuaries, India
You can study for a Bachelor’s / Master’s / Doctoral degree in any of the following fields (Note that all these fields may not offer you a degree at all three levels, that is in Bachelor’s, Master’s and Doctoral. Some fields may offer a degree only at the Master’s or at the Doctoral level):
1. Financial Mathematics
2. Financial Engineering & Technology
3. Financial Management
4. Financial Economics
5. Mathematics and Statistics
6. Actuarial Science
7. Actuarial Mathematics
8. Computational Economics
9. Financial and Capital Markets
10. Financial Analysis
11. Applied Statistics
12. Applied Mathematics
13. Econometrics and Quantitative Economics
14. Computer Science Engineering
15. Financial Economics
16. Quantitative Economics
UGC has recently recognised the CA/CS/ICWA Qualifications as equivalent to Postgraduate Degree.
Competencies Required
Interests
1. You should have interests for Investigative Occupations. Investigative occupations involve working with ideas and quite a lot of thinking, often abstract or conceptual thinking. These involve learning about facts and figures; involve the use of data analysis, assessment of situations, decision making and problem-solving.
2. You should have interests for Conventional Occupations. Conventional occupations involve repetitive and routine tasks as well as fixed processes or procedures for getting things done. These occupations involve working more with data, systems, and procedures and less with ideas or creativity.
Knowledge
1. You should have knowledge of Mathematics – Knowledge of arithmetic, geometry, trigonometry, and other mathematical disciplines and their applications.
2. You should have basic programming skills in Python and knowledge of basic algebra (algebraic concepts such as functions & variables), basic statistics, linear algebra, and calculus which are all frequently used in programming.
3. You should have knowledge of Computers - Knowledge of computer hardware and software, computer programming, computer networks, computer, and mobile applications.
4. You should have knowledge of Economics - Knowledge of economic principles and practices; understanding how various resources such as land, labor, and capital are used; how market demands rise and fall; how a country collects and spends money; and similar other economic issues and situations.
5. You should have knowledge of Accounting - Knowledge of various principles and methods for maintaining records of commercial and financial transactions and records, preparing various reports and statements, ensuring compliance with commercial and business laws and rules of a country, etc.
6. You should have knowledge of analytical and scientific software such as IBM SPSS Statistics, Insightful S-PLUS, SAS, StataCorp Stata, The MathWorks MATLAB, etc; business intelligence and data analysis software such as MicroStrategy, etc.
7. You should have knowledge of tools such as R, Python, SQL, Tableau, Visier, Salesforce and Excel to drive analytics and knowledge of Earned Value Management Systems (EVMS) processes and practices.
Skills
1. You should have Systems Analysis Skills - determining how a system should work and how changes in conditions, operations, or the environment will affect outcomes.
2. You should have Systems Evaluation Skills - identifying measures or indicators of system performance and the actions needed to improve or correct performance, relative to the goals of the system.
3. You should be skilled in Computer (Data Analysis and Visualisation) - using SPSS, SAS, SAP Hana, IBM Cognos, MATLAB, Minitab, Google Analytics, RapidMiner, R, Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Tableau, Visual Basic, etc.
4. You should have Quality Control Analysis Skills - conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
5. You should have Critical Thinking skills - Skills in the analysis of complex situations, using logic and reasoning to understand the situations and take appropriate actions or make interpretations and inferences.
6. You should have Judgment and Decision Making Skills - considering pros and cons of various decision alternatives; considering costs and benefits; taking appropriate and suitable decisions.
7. You should have Problem Solving Skills - Skills in analysis and understanding of problems, evaluating various options to solve the problems and using the best option to solve the problems.
8. You may need Programming Skills - writing computer programs for various applications, installation of computer programs and troubleshooting of problems in computer programs or software.
Ability
1. You should have Deductive Reasoning Ability - apply general rules and common logic to specific problems to produce answers that are logical and make sense. For example, understanding the reasons behind an event or a situation using general rules and common logic.
2. You should have Problem Sensitivity - The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
3. You should have Inductive Reasoning Ability - to combine pieces of information from various sources, concepts, and theories to form general rules or conclusions. For example, analyzing various events or situations to come out with a set of rules or conclusions.
4. You should have Information Ordering Ability - to arrange things or actions in a certain order or pattern according to a specific rule or set of rules (e.g., patterns of numbers, letters, words, pictures, mathematical operations).
5. You should have Fluency of Ideas - The ability to come up with several ideas about a topic (the number of ideas is important, not their quality, correctness, or creativity).
Personality
1. You are always or mostly careful about your actions and behavior.
2. You are always or mostly disciplined in your action and behavior.
3. You are always calm or generally remain calm in most situations.
4. You are imaginative sometimes.
5. You are always or mostly organised in your day-to-day life and activities.
Career - Job Opportunities & Profiles
1. Work in this field is very diverse. Top finance jobs primarily demand an astute decision-maker. There is a tremendous amount of fluidity between different financial-engineering careers with a wide range of pay as well as the transferable skills that allow professionals to easily move between the many opportunities in this field.
2. You, as a Financial Engineer, may pursue professional roles such as a quantitative researcher, quantitative developer, quantitative trader, algorithmic trader, and portfolio analyst or other similar job roles for financial institutions.
3. You may start as a Portfolio Implementation Intern/ Finance Management Trainee/ Analyst Trainee or similar positions at the training level before entry-level job roles. Then you may proceed to following entry-level positions after your internship or traineeship.
You may, as well, surpass the internships or traineeships to join in any of these positions if you have relevant advanced qualifications as preferred by your employer.
1. Finance Engineer
2. Finance Analyst
3. Portfolio Implementation Analyst
4. Business Impact Engineer
5. Quantitative Research Analyst
6. Cost Analyst
7. Financial Quantitative Analyst
8. Analyst - Risk & Info Management
9. Workforce Analytics Researcher
10. Business Impact Analyst
11. Actuarial Assistant/ Associate
12. Associate - Corporate Finance
13. Investment Strategist
14. Quantitative Strategy Analyst
15. Analyst – Asset Management
16. Business Operations Analyst
17. Finance Systems Analysis and Change - Analyst
18. Specialist – Public Finance
19. You may work for some of the most prominent financial firms and companies in the world, such as Goldman Sachs, Barclays, and AIG.
20. You may work with major global players offering financial analytics and related services including Oracle, IBM, Teradata, SAP (Germany), Qlik, Google, Information Builders, Zoho Corporation etc.




21. You may work for financial inclusion consulting firms, private investment firms, multinational investment banks, insurance companies or financial services companies operating in the field of investment management, financial advisory services, securities, asset management, prime brokerage, insurance services and securities underwriting such as MicroSave, JP Morgan Chase, Muthoot Finance, TATA Capital, Morgan Stanley, BAJAJ Finserv, Handstand India Ltd. etc.



22. You may work with corporations/ enterprises/ consulting agencies which specialize in mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, activist shareholder, capital-raising services and takeover defense, and other related advisory services such as Houlihan Lokey etc.
23. You work may also be focused on public policy, working for governments developing financial policies, or conducting research at think tanks. Your government department may also sponsor you to Diploma programs to specialize in a particular area.
24. You may work with global organizations/ banks such as World Bank, Citi Group, HSBC or Deloitte, American Express Company etc.



25.You may work with Finance & Business Operations (F&BO) teams at technology biggies such as Lockheed Martin Corporation (manufacturing industry), Alcoa Corporation (global leader in bauxite, alumina & aluminum products), Tesla (sustainable energy behemoth) or similar.
Career Growth
1. If you join as a Trainee Analyst/ Research Intern/ Graduate Intern/ Program Intern, then after completion of your training, you will be positioned as Finance Engineer/ Finance Analyst/ Portfolio Implementation Analyst/ Business Impact Engineer/ Quantitative Research Analyst/ Cost Analyst or in similar positions.
2. However, if you join after your post-graduation or higher advanced qualifications in a relevant discipline, you can surpass traineeship/ internship to directly get a job as any one of these positions.
3. After 6-12+ years of experience, you can expect to become a Senior Financial Modeling Analyst, Senior Business/Finance Analyst, Strategy & Marketing; Principal Business Analyst; Deputy Manager/ Associate Manager; Finance & Business Analytics Manager; Group Manager; Member of Technical Staff; Head - Risk Analytics & Engineering; or similar roles.
4. Then after 15-20+ years of experience, you may grow as a Senior Manager; Associate Vice President; Area Vice President; Vice President, Finance; Senior Vice President, Technology Risk; Corporate Vice President, Strategy & Internal Consulting; Global Head of Finance Services/Operations; Vice President, Marketing Analytics & Data Science; Director, Planning & Delivery; Director of Business Insights; Senior Director, Global Customer Success; Global Partner Director; CEO or similar roles.
Salary Offered
1. At the entry-level jobs with private companies, you may expect to get about: Rs. 50,000 – 2,50,000 or even more a month (higher sides by MNCs to premier institution graduates).
2. In junior level jobs (after 5+ years of experience), you can make about Rs. 70,000 – 4,00,000 or more per month.
3. In mid-level jobs with private companies in India, you can expect to earn about Rs. 1,50,000 – 8,00,000 or even more a month.
4. In senior-level jobs with private companies in India, you can expect to earn about Rs. 2,50,000 – 12,00,000 or even more a month.
5. All higher ranges are by MNC Consulting firms/ Financial institutions and lower ones by mid-scale Indian companies/ public sector banks and financial institutions.
Global (US)
At the entry-level jobs, after your Master's degree depending upon the institution where you are graduating from, you may expect to get about, USD 2500 – 6200or, even more, a month. Work opportunities are moderately rare for graduates from India who have completed their post-graduation in the US. Many recruiters operating in this field will require you to be a green card holder, national citizen or a permanent resident in the country.
However, if you can obtain an advanced degree (in Structured Finance, Derivatives & Risk Management, Investment Banking, Quantitative Finance, International Finance, Corporate Governance, Firm Valuation, Taxation Law & Practice, etc.) after your post-graduation in a relevant discipline there, you may start with temporary or assistive roles like that of a Graduate/ Doctoral/ Higher Level/ Part-time Teaching Assistant or Graduate Program Assistant or Summer Intensive Instructor or at similar positions and then gradually work your way up the ladder.
For larger MNCs (think Morgan Stanley, Google, IBM, SAS, etc.) with operational units in India, you may be placed on a temporary/ contractual basis for project-based work at international locations while you are permanently posted in India. Some do get permanently transferred to such locations too however that is few and far between.
With junior level jobs, you may expect to earn around USD 4000-8500a month or more depending on your job location and roles.
In mid-level jobs, you can expect to earn about USD 5000 – 10200or, even more, a month.
In senior-level jobs, you can expect to earn about USD 6500-12500or, even more, a month. Senior corporate leadership positions such as the roles of Global Head of Finance or Director of Business Insights get much more than this (usually a 7-figure sum); their total remuneration including performance bonuses could be as high as 2 million dollars a year.
Monthly Earning in Indian Rupee
1. Entry level: 0 - 2 years of work experience
2. Junior Level: From 1 to 12 years of work experience
3. Mid-Level: From 5 to 20+ years of work experience
4. Senior Level: From 10 to 25+ years of work experience (there could be exceptions in some high-end technical, financial, engineering, creative, management, sports, and other careers; also in the near future, people will reach these levels much faster in many careers and in some careers, these levels will have no meaning as those careers will be completely tech skill driven such as even now, there is almost no level in a Cyber Security Expert’s job)
Work Activities
1. Analyzing and interpreting data and information - Analysis of data and information to find facts, trends, reasons behind situations, etc.; interpretation of data to aid in decision making.
2. Computing - using various computer software applications; writing algorithms for various computer and mobile applications; using software applications for scientific and technical work.
3. Creative thinking - Developing new ideas, concepts, innovative solutions to problems, newer ways of getting things done, designing products and services, creating work of art and craft, etc.
4. Getting Information and learning - Observing, hearing, reading, using computers, or otherwise obtaining information and learning from it.
Making decisions and solving problems - Analysis of data and information; evaluation of alternative decisions and results of decisions; taking the right decisions and solving problems.
5. Organizing, planning and prioritizing tasks - Planning and organizing tasks in order to achieve work goals; prioritizing tasks to achieve goals and making the best use of the time available.
6. Processing Information - Compiling, tabulating, calculating, auditing, verifying or otherwise dealing with information processing including data entry, transcription, recording, storing and maintaining databases.
7. Strategic planning - Developing visions and goals, developing strategies and action plans for achieving visions and goals.
8. Updating and using relevant knowledge - Keeping updated with the latest knowledge relevant to your fields of work and use of the relevant knowledge in getting things done.
9. Using computers for work - Using computers for day-to-day office work; using computer software for various applications in day-to-day professional work; entering data and process information; for writing.
10. Working in a team - Working in a team of people; developing team; maintaining professional relationships among team members.
11. Working with computers, programming and performing technical tasks - Using computers and computer systems, hardware, and software for programming, developing software and/or hardware, developing computer applications, systems, and networks; developing mobile applications.
Future Prospects
1. The future of this pathway seems extremely bright especially as the industry statistics are very encouraging.
2. The adoption of financial analytics for scalability, white-space mapping, customer relations and fraud detection & prevention (by screening wire transfers, checks, fund transfers, deposits, & withdrawals) across major industries has propelled the demand of financial engineers and quantitative economists spanning all these sectors.
3. The Global Financial Analytics Market is expected to grow from USD 6.9 billion in 2018 to USD 11.4 billion by 2023, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7%. The key growth factor is the emergence of new IT applications & infrastructure such as big data and advanced analytics.
4. The Digital Money Transfer & Remittance market value is projected to display a robust growth represented by a CAGR of 11.75 % by value during 2019-2024. Enormous data generation and the need for interactive analysis are primarily driving the demand for competent & adequately trained professionals in this field.
5. The Global Financial Services Application Market was valued at over USD 79 Billion in 2018 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.8% by 2024. The major players include Fidelity National Information Services Inc., Accenture Inc., Tata Consultancy Services Limited, Fiserv Inc., Infosys Ltd and IBM (International Business Machines Corporation). TCS is the only Indian player.
6. The Global Debt Collection Software Market is expected to grow from USD 2,386.89 Million in 2018 to USD 4,123.51 Million by the end of 2025 at a CAGR of 8.12%. The Global AI in Fintech Market is expected to grow from USD 2,683.68 Million in 2018 to USD 16,963.55 Million by the end of 2025 at a CAGR of 30.13%.
7. The global Structured Finance Market is poised to grow at a CAGR of 16.49% during 2016-2020. The Global P2P (Peer to Peer) Lending Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 53.06% during 2016-2020.
FUTURE PROSPECTS AT A GLANCE